Mehtodology
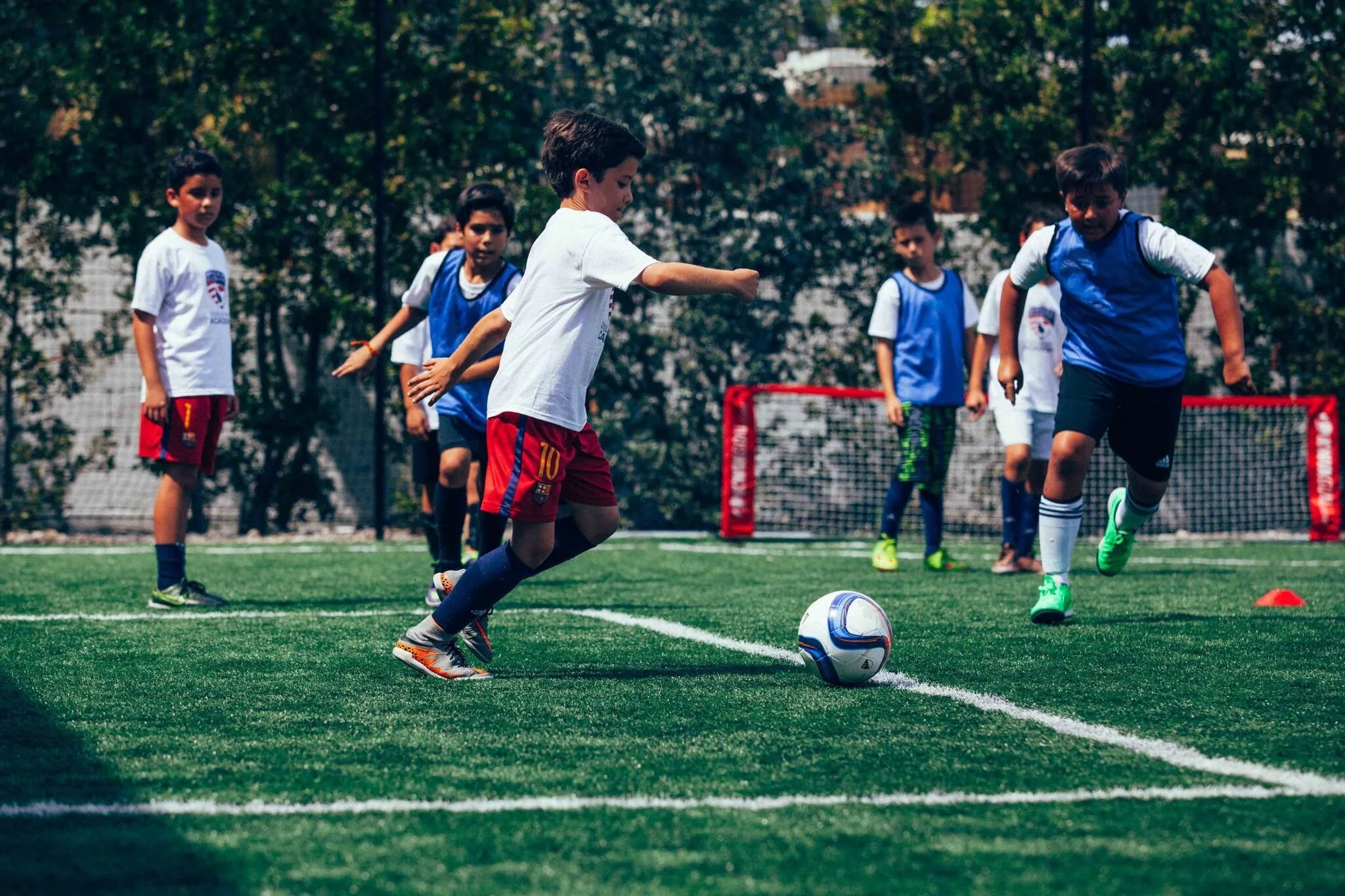
The game of soccer is a sequence of complex and unpredictable game situations performed by 11 v 11 players. During a game, players are responsible for making thousands of decisions. Because of these game characteristics, soccer is a sport that cannot be controlled by the coach from the side-lines. . Therefore, from a decision-making point of view, Soccer is a players’ sport. Soccer is spomtaneous sport.
Players must be taught how to think, PLAYER IQ… PHYSICAL CONDITONIONG ALONE WILL NOT WIN A GAME>>>building positive problem-solving habits on the training ground elevates players to perform to their full potential on match day. Football players develop better and quicker when having to deal with setbacks and the need to solve problems as this is exactly what happens during the game.
They must get the freedom to learn, to make decisions and to take responsibility, freedom within the clear tactical reference of the coach.
Mental speed is important, as decisions must be made in a fraction of the time; mental speed is what separates elite players from the average.
How CAN WE DEVELPO THIS.. RONDOS ETC>>>>
Take a host of Spanish players as an example: Xavi, Iniesta, Busquets, David Silva or Xabi Alonso, none of them has outstanding physique or explosive power, yet they are/were role defining players. Much like chess masters, they read the game, are aware
Soccer IQ is a concept that encompasses a player's understanding of the game, including tactical awareness, decision-making, and anticipation of opponents' moves. It is often said that players with high Soccer IQ have an innate ability to read the flow of the game, making them valuable assets to their teams.
Key components of Soccer IQ include:
Tactical Awareness: Understanding formations, positioning, and the roles of teammates and opponents. A player with good tactical awareness knows where to be at any given moment and how to best support the team's strategy.
Decision-Making: This involves selecting the best course of action in a split second, whether that means passing, shooting, or transitioning between defense and attack. High Soccer IQ players analyze their options quickly and execute the most effective choice.
Anticipation: Players with high Soccer IQ can predict the movements of opponents, allowing them to intercept passes or position themselves effectively. This foresight often leads to creating scoring opportunities or preventing goals.
Situational Awareness: Understanding the context of the game, such as time left on the clock, score differential, and player fatigue. This awareness can guide decisions that align with the team's immediate goals.
Communication: Effective verbal and non-verbal communication with teammates fosters better teamwork and helps maintain tactical discipline. Players with high Soccer IQ often excel in guiding their teammates and organizing defensive efforts.
Improving Soccer IQ can be achieved through several methods, including watching game footage, participating in tactical discussions, and gaining real-time experience on the field. Coaches can play a significant role by emphasizing the importance of these skills in practice sessions and encouraging players to think critically about their gameplay.
In summary, developing Soccer IQ is vital for individual players and team performance. It allows players to complement their technical abilities with a deeper understanding of the game, leading to more dynamic and successful play.
Soccer IQ can be developed through a combination of theoretical understanding, practical experience, and mental exercises. Here are several strategies to enhance soccer IQ:
Watch Games Critically: Analyze professional matches by focusing on team formations, player movements, and decision-making processes. Pay attention to how players read the game and respond to different situations.
Study Tactics: Learn about various formations and strategies used in soccer. Reading books, articles, and watching instructional videos can provide valuable insights into tactical understanding.
Participate in Discussions: Engage in conversations with coaches, players, and analysts to gain different perspectives on the game. Discussing plays and strategies can deepen understanding and encourage critical thinking.
Play Regularly: Consistent practice is essential. Playing in different positions can provide a broader perspective of the game, helping players to understand various roles and responsibilities on the field.
Analyze Personal Performance: After games or practices, review personal and team performance. Identify decision-making moments where the player could have acted differently, and consider alternative options.
Use Visualization Techniques: Mental rehearsal can enhance game understanding. Visualizing scenarios, such as breaking down a defensive setup or executing set plays, prepares players for real-time decision-making.
Engage in Small-Sided Games: Participating in small-sided games fosters quick thinking and decision-making under pressure. These formats allow players to experience a higher volume of touches and interactions.
Focus on Positional Awareness: Develop an understanding of space and positioning. Recognizing where to be at any moment can significantly improve a player's impact on the game.
Analyze Statistics and Data: Familiarize yourself with key performance indicators in soccer, such as possession statistics, passing accuracy, and player heat maps. Understanding these metrics can enhance strategic thinking.
Seek Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from coaches and peers to identify areas for improvement. Constructive criticism can help players refine their understanding of the game.
Developing soccer IQ is a continuous process that involves commitment and curiosity. By integrating these strategies into training and gameplay, players can enhance their cognitive abilities on the field.
Rondos
Our methodology incorporates Rondos as one of our teaching elements. Rondos are the perfect tool to coach all elements of the game. Through numerous touches on the ball players learn the basics of correct positioning, width, depth, length, passing, receiving, mobility, agility, balance, quick decisions making and keeping the ball under pressure.
Rondos are effective due to the close proximity that they are played in, this forces players to increase their vision and mental processing speed, all qualities that are necessary to succeed on a full size field. Players must continuously identify and make decisions with respect to the constantly changing environment.
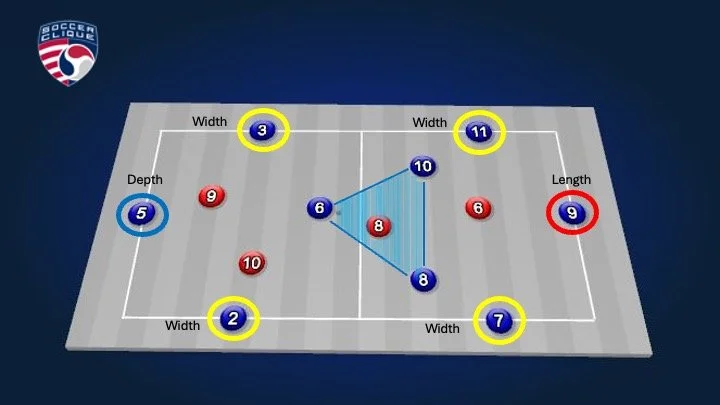
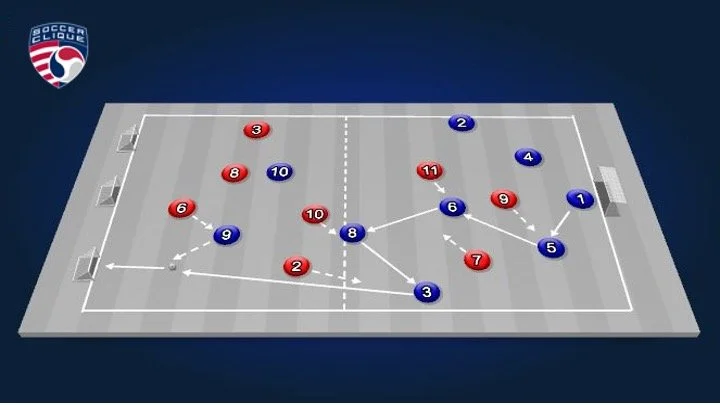
Rondo 9 v 4 | Space Awareness, Width, Depth, Length and Triangulation
There are numerous varieties of Rondos to effectively teach specific game concepts One example are Positional Rondos, where players occupy common field areas to their respective positions, with technical, tactical and physical loads adjusted to position-specific activities.
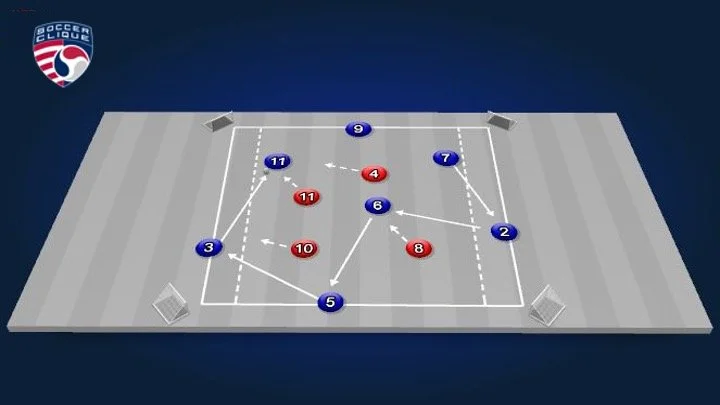
Positional Rondo | 7 v 4 Attacking Transitions
Everything that happens in a soccer match can be trained with a variety of Rondos.
Soccer rondos are training exercises aimed at improving players' skills, decision-making, and teamwork. In a rondo, players form a circle while one or more players in the center attempt to regain possession. The outer players pass quickly to maintain control.
Purpose of Rondos
Technical Development: Enhances footwork, passing accuracy, and ball control under pressure.
Game Awareness: Encourages awareness of passing options and anticipation in defenders.
Fitness and Agility: Provides cardiovascular workouts, requiring agility and stamina.
Key Points
Number of Players: Typically five to ten, with smaller groups focused on skills and larger groups on tactics.
Space and Setup: Area size can vary; smaller spaces promote quick passing, while larger spaces allow for movement.
Variations: Rules can be adjusted, such as limiting touches or setting time constraints.
Conclusion
Incorporating rondos into training benefits players of all ages and skill levels, enhancing technical ability and teamwork.
Positional-Possession Games
Our methodology uses positional play based training in order to teach our players how to position themselves in relation to their teammates, the opponents and the ball.
The purpose is to create numerical advantages against the opponents throughout the entire field of play by always having one more passing option than the total number of defensive players pressing the ball.
Players are positioned in triangles or diamonds in order to provide diagonal passes which overplay horizontal and vertical lines and are more difficult to defend and allow for easier ball progression through the thirds of the field.
Players are positioned on horizontal and vertical planes in order to create passing options for the player in possession of the ball and to create as much length and width as possible. The objective is to always offer the ball-carrier at least two passing options.
Players must move based on the movement of a teammate. This creates constant player rotation that aims to disrupt the opponents.
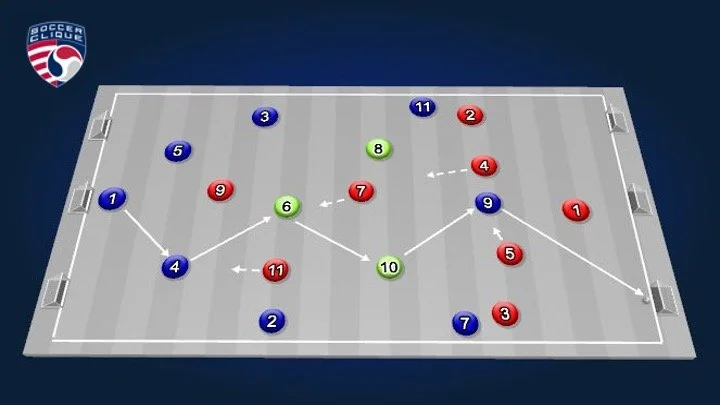
Positional Game | 8 v 8 +3 - Control and Possession
A Possession based principal of play is a key component in order to be successful in Positional play. This is why you see both Positional play and Possession play grouped together. Although, they are different in their application one of the key elements of an effective Positional play strategy if for a team to be able to play a Possession based style of play.
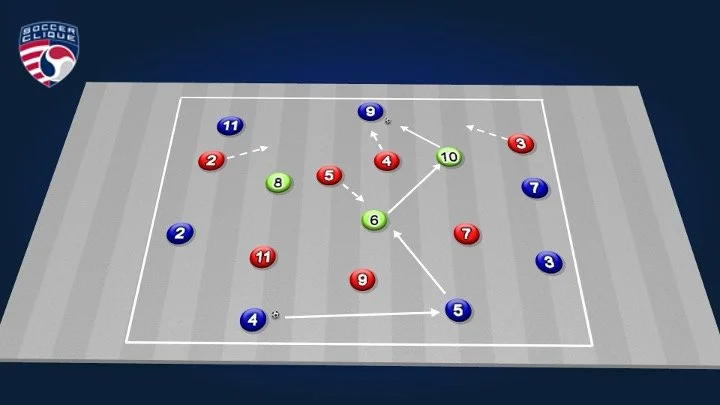
Possession Game | 7 v 7 +3
Possession games are a fundamental training method used in soccer to enhance players' ability to maintain control of the ball under pressure. These drills typically involve a smaller field and a limited number of touches, emphasizing quick decision-making, tactical awareness, and teamwork.
In possession games, teams are tasked with keeping the ball away from an opponent while progressing it towards designated targets or areas. Common variations include "Rondo," where a small group of players in the center aims to maintain possession against a larger group on the outside trying to intercept the ball, and "Keep Away," which focuses on maintaining possession while moving the ball strategically around the field.
These drills encourage players to work on critical skills such as passing accuracy, spatial awareness, and communication. Additionally, they help develop a player's ability to read the game, anticipate opponents' movements, and create passing lanes. As players cycle through different positions in various exercises, they gain a comprehensive understanding of how to control the tempo of the game.
Possession games can be tailored to fit different age groups and skill levels, ensuring that players remain engaged and challenged. Coaches often implement specific rules or conditions, such as limiting the number of touches or requiring certain types of passes, to focus training on particular aspects of ball control and teamwork.
Overall, possession games serve as an effective tool for fostering essential skills that translate well into match situations, promoting both individual development and team cohesion.
Soccer positional games, often referred to as rondos or possession drills, are an essential training method that focuses on improving team dynamics, ball control, and spatial awareness. These drills typically involve a small group of players maintaining possession of the ball while other players attempt to retrieve it.
Types of Positional Games
Rondos
Structure: A common setup involves a circle or square where a set number of players keep the ball away from one or two defenders.
Focus: Emphasizes quick passes, movement off the ball, and decision-making under pressure.
Keep Away
Structure: Similar to rondos but can be done in larger areas. Players must maintain possession while defending against one or two players.
Focus: Develops teamwork, communication, and tactical awareness as players create passing angles and space.
Overloads
Structure: A defined area where one team has more players than the other. The goal for the overloaded team is to retain possession, while the defending team aims to win the ball.
Focus: Improves positional awareness, off-the-ball movement, and the ability to press as a unit.
Conditioned Games
Structure: Small-sided games with specific conditions, such as only allowing touches on one side of the field or requiring a certain number of passes before a goal can be scored.
Focus: Instills tactical discipline and sharpens specific skills relevant to game scenarios.
Benefits of Positional Games
Develops Technical Skills: Players enhance their passing, receiving, and dribbling abilities in a dynamic environment.
Enhances Tactical Understanding: Players learn to read the game, anticipate opponents' movements, and position themselves effectively.
Encourages Team Cohesion: Practicing in small groups fosters closer teamwork and better communication among players.
Adapts to Game Pressure: Simulating game scenarios prepares players to handle real match situations with confidence.
Implementation in Training
To incorporate positional games effectively into training sessions:
Set Clear Objectives: Define the skill or tactical focus for the session (e.g., building out from the back, pressing).
Ensure Progressive Difficulty: Start with simpler drills and gradually introduce more complexity as players become comfortable.
Maintain Energy Levels: Keep sessions dynamic and engaging to maintain player enthusiasm.
Provide Feedback: Offer constructive feedback to help players understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
Positional games are versatile and can be adapted for all ages and skill levels, making them a vital tool for coaching in soccer. By consistently integrating these drills, teams can develop a more cohesive, skilled, and tactically astute squad.
Small Sided games
Small-sided soccer games, typically involving fewer players on reduced-sized fields, offer various benefits for players of all ages and skill levels. These games vary in format, commonly played 3v3, 4v4, or 5v5, and are designed to enhance critical aspects of the game.
One of the primary advantages of small-sided games is the increased opportunity for touches on the ball. With fewer players, individuals have more room to maneuver and engage with the ball, which leads to improved ball control, dribbling skills, and passing accuracy. This exposure helps build confidence in players as they can experiment with different moves and techniques.
Moreover, small-sided soccer promotes a greater understanding of the game. Players are often required to make quick decisions and adapt to changing situations, fostering better tactical awareness. They learn to read the game as they face various defensive setups without the luxury of extra teammates to rely on, enhancing their problem-solving skills in real time.
Additionally, small-sided games encourage teamwork and communication. With fewer players on the field, each individual's role becomes more prominent. Players must work closely together, strategizing and coordinating their efforts to be successful. This collaborative aspect can be especially beneficial for youth players, as it teaches them the importance of supporting one another both on and off the ball.
Physical fitness is another crucial element enhanced by small-sided games. The fast-paced nature of these matches requires players to stay active and engaged, providing an excellent cardiovascular workout. The compact playing area encourages constant movement, which can improve speed, agility, and overall fitness levels.
In summary, small-sided soccer games are a valuable aspect of soccer development. They facilitate skill enhancement, tactical understanding, teamwork, and physical fitness, making them an essential tool for coaches and players looking to improve their game.
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae. In sit amet felis malesuada, feugiat purus eget, varius mi. Donec ac fringilla turpis.sadvsDFGJDOVJNosdfinoDVNOADVNXOVNASIGomdfvoncxobk
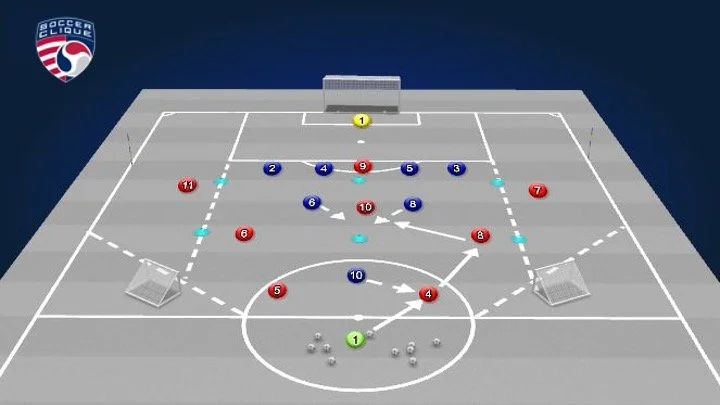
Conditioned Game | 8+ GK v 8 Playing out from the back
Conditioned Game | 8 v. 8 Defending the Overload